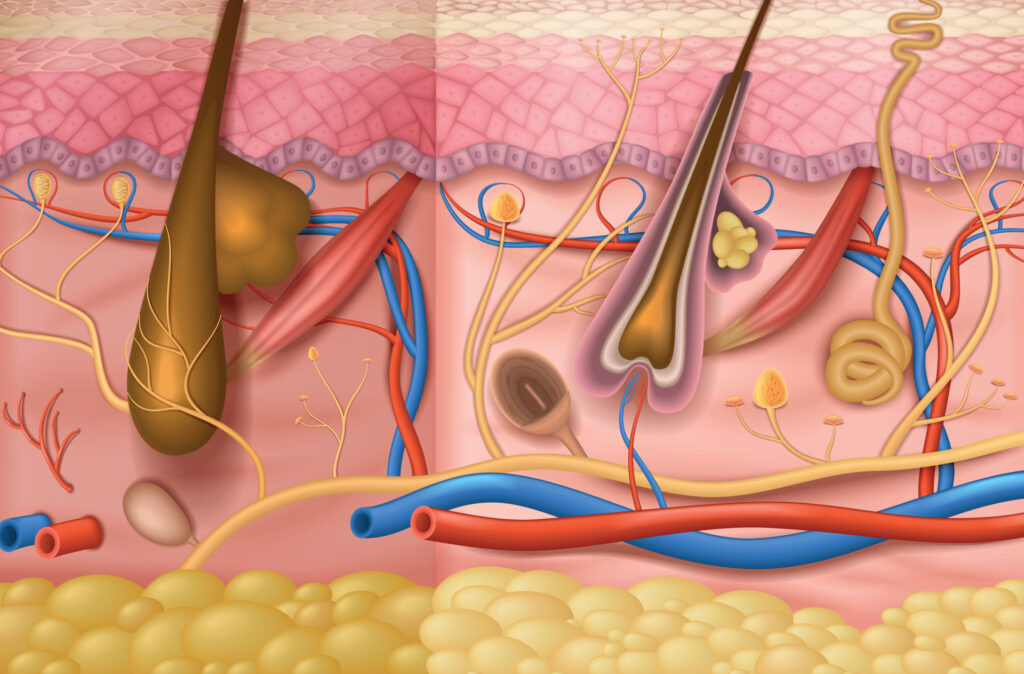
Stem cell therapy has traditionally been known to provide benefit to patients suffering from knee pain, multiple sclerosis, and other degenerative disorders. However, the regenerative capabilities of stem cells extend far beyond this domain. Just as stem cells work to heal and regenerate damaged tissues, the bioactive molecules released by stem cells can be used in topical treatments for the skin.
However, some cosmetics companies have taken advantage of this optimism towards stem cell therapy through deliberately vague and misleading advertising. Many of these firms claim that their products contain stem cells that will rejuvenate and restore a more youthful appearance to the skin.
Unbeknownst to the consumer, simply incorporating cultured stem cells into a serum or cream does not confer the rejuvenating properties advertised. Stem cells – as is typical for all types of cells – die within hours when removed from their culture conditions, rendering them useless as they degrade in the cosmetic product. To better understand this concept, imagine a severed limb that is detached from the body: one wouldn’t expect this limb to “reanimate” after a significant time of separation. Similarly, stem cells are unable to survive when deprived of the key nutrients and environmental factors provided by the rest of the body.
Conditions For Live Stem Cell Survival
Stem cells require highly specific culture conditions, monitored and calibrated rigorously by highly trained scientists, to keep them alive and healthy.
Chief among these are:
- Specific concentrations of CO₂ and oxygen
- Neutral pH
- Consistent temperature of 37°C
- A liquid called “culture medium,” which contains amino acids, sugars, vitamins, and hormones.
These components would typically be provided by the body, to promote the survival and proliferation of the stem cells. When transferred to a container, which is either kept on a store shelf or shipped out, the cells are subjected to rapidly fluctuating temperatures, to keep the cells alive and allow them to proliferate. These key requirements cannot be met by a product kept in a container at room temperature on a store shelf, or in the rapidly fluctuating temperatures packages are subjected to during shipment.
“For any type of stem cell to be of any use whatsoever, the cells must be alive. The processing needed to incorporate living cells into any type of cream or serum would inevitably kill them, rendering them useless.”
For these reasons, it is impossible to distribute consumer-grade products containing live stem cells. A team of scientists led by RegeneVive Chairman, Co-Founder, and Chief Scientific Officer Dr. Anand Srivastava, however, discovered that 80% of the healing capabilities of stem cells are derived from the release of multiple molecules into the damaged skin. These molecules, which include cytokines, antioxidants, and growth factors, help improve skin appearance by promoting new cell growth, synthesis of proteins that support skin structure such as elastin and collagen, and attract immune cells that remove damaged cells, all while also reducing inflammation.
By this method, cytokines and growth factors that would normally be released by stem cells into the surrounding body tissues, are released into the culture media. These molecules can be taken from this environment and incorporated into skincare products, while still maintaining their bioactive capacity to restore the appearance and integrity of the skin.
Methods of Harvesting
Plastic surgeons are experts in wound healing, a process in which stem cells play a prominent role. Doctors have long used the technique of extracting fat from the body and injecting it into hollowed-out or depressed areas of the face to fill in injuries, correct wrinkles, and improve the face’s curvature. Lipotransfer, or the harvesting of body fat and injecting it into the face, has been around for many years in traditional plastic surgery clinics. In recent years, some plastic surgeons have started to cull stem cells from fat. One procedure that does just that is called cell-assisted lipotransfer (CAL).
CAL involves the harvesting of adipose tissue (or fat) via liposuction, typically from the patient’s lower abdomen. Fat contains stem cells that can differentiate into several cell types, including skin, muscle, cartilage, and bone. Fat tissue has an especially stem cell-rich layer. These cells are then mixed with some regular fat, making in effect a very stem cell-rich fat solution, right in the doctor’s office. The process of manipulating the fat cells takes about 90 to 110 minutes, and then the solution is ready to be injected into the skin, to fill in the lips, the cheeks, and the nasolabial folds, or the deep folds around the nose and mouth.
Some experts maintain that the cell-enriched fat provides better, longer-lasting results than those of regular fat, which is often injected into the face. The tissue graft grows its own blood vessels, a unique advantage which may increase its longevity.
Want to Learn More?
RegeneVive continues to lead the field of regenerative medicine, discovering new capabilities and applications of stem cells. In addition to successfully treating a severely ill COVID-19 patient (under the FDA’s expanded access for compassionate use program), our team has conducted groundbreaking research on psoriasis and other skin disorders. Our skin serum, which leverages BAM technology, showed a more than 31% higher score when evaluated in studies against several state-of-the-art skincare products on the market.
To learn more about our innovative work in skincare, please visit our pages on this topic, or email [email protected].
